PHARMACY CLEANROOM SOLUTION
Ensure full compliance with U.S. regulations for compounding pharmacies with our turnkey cleanroom solutions.
Why Pharmacies Need USP-Compliant Cleanrooms
Pharmacies in the United States are required to follow USP <797> and USP <800> standards for compounding sterile and hazardous drugs. These regulations aim to ensure the safety of patients and healthcare workers, minimize contamination risks, and control exposure to hazardous substances.
Common pharmacy challenges:
Maintaining ISO-classified environments
Preventing cross-contamination between hazardous and non-hazardous areas
Managing air pressure differentials and airflow
Providing proper gowning and material transfer procedures
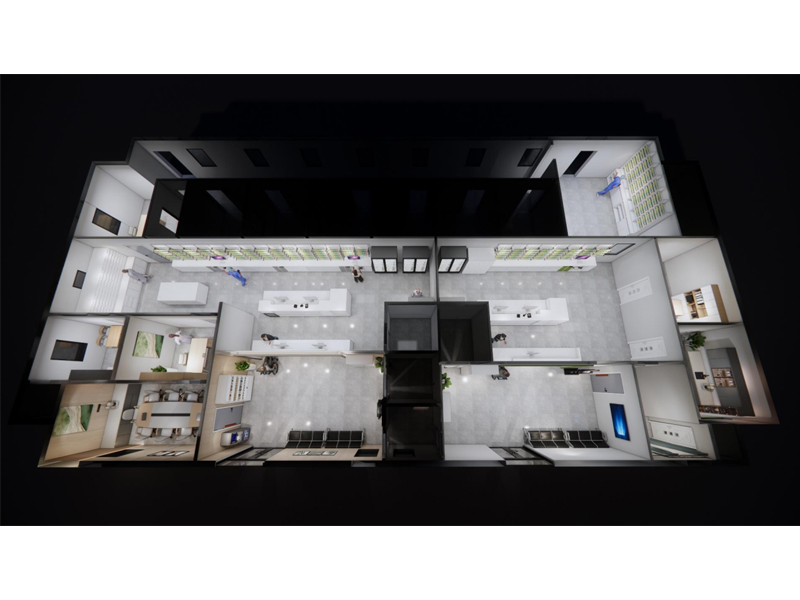
Layout for USP 797 / USP 800 Cleanrooms
Designing a pharmacy cleanroom that complies with USP <797>, USP <800>, FDA, and OSHA regulations requires meticulous zoning and airflow control. Each area must support specific operational goals — preventing drug contamination and protecting personnel from hazardous exposure.
| Standard | Purpose | Area Type | Air Pressure | Airflow |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USP <797> | Prevent product contamination | Non-hazardous compounding | Positive | Recirculated |
| USP <800> | Protect personnel from hazardous exposure | Hazardous compounding | Negative | Exhausted outdoors |
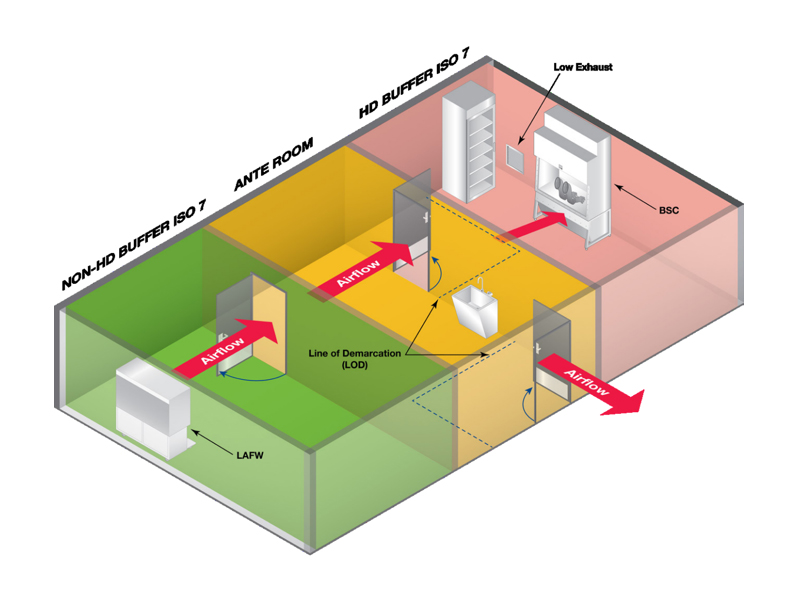
Cleanroom Zoning Overview
A USP-compliant cleanroom typically includes the following functional areas:
Ante Room (ISO 7/8)
Gowning area for donning personal protective equipment (PPE)
Clearly marked dirty vs. clean zones on the floor
Hand washing sink located ≥1 meter from the entry door
Eye wash station near hazardous areas
Serves as a transition zone to both non-HD and HD rooms
Non-Hazardous Compounding Room (ISO 7)
Positive pressure relative to the Ante Room
Equipped with Laminar Airflow Workbenches (LAFWs)
HEPA-filtered air; supports sterile preparation of non-HD drugs
Hazardous Drug Compounding Room (ISO 7)
Negative pressure relative to adjacent rooms
Exhaust air is non-recirculated and vented outside
Contains Class II Type B2 Biological Safety Cabinets (BSCs)
Buffer Room (ISO 7)
Supports both HD and non-HD rooms
Stable temperature and humidity environment
Houses air handling units and support equipment
HD Storage Room (ISO 7/8)
For segregated storage of hazardous drugs
Access from the ante room in the same airflow direction

Flow & Layout Principles
neutral/ante →Clean areas → Dressing Area → Buffer → Sterile preparation area

Industry Background & Pain Points
High sterility requirements:
Microbial and particle contamination must be avoided during drug preparation.
High compliance pressure:
Stringent standards such as FDA, EU GMP and USP <797> need to be met.
Difficult expansion:
Existing facilities are difficult to meet the needs of business growth.
Our GMP Pharmacy Cleanroom Solutions
Customized design:
Customize cleanroom layout and functions according to pharmacy needs.
Compliance guarantee:
Cleanrooms comply with FDA, EU GMP and USP <797> standards.
Flexible expansion:
Modular design supports later expansion and upgrade.


